Materials:
FDM printers typically use thermoplastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) or ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene). Different materials have unique properties, strengths, and use cases


Printer Settings:
Parameters like layer height, print speed, and temperature are crucial for achieving optimal print results. Understanding these settings can help you fine-tune your prints.
Printing Troubleshooting:
Issues such as layer adhesion problems, warping, or under-extrusion are common in FDM printing. Knowing how to troubleshoot these problems can improve your printing experience.

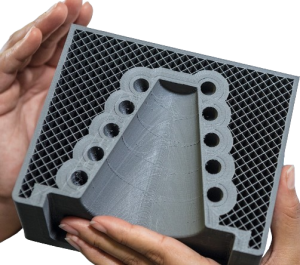
Model Design:
Preparing 3D models for printing involves considerations like orientation, support structures, and tolerances. Certain design practices can enhance the printability of your models.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printing is a popular type of 3D printing technology. FDM printing is widely used for prototyping, hobbyist projects, and low-volume production due to its affordability, simplicity, and versatility. However, it may have limitations in terms of surface finish and dimensional accuracy compared to other 3D printing technologies.

